- 摘要
- 如何理解 VDom?
- 如何表示 VDom?
- 如何比较 VDom 树,并且进行高效更新?
- 变量的含义
- 情况 1:新增节点
- 情况 2:删除节点
- 情况 3:变化节点
- 情况 4:递归对子节点执行 Diff
- 效果观察
- 参考链接
摘要
随着 React 的兴起,Virtual DOM 的原理和实现也开始出现在各大厂面试和社区的文章中。其实这种做法早在 d3.js 中就有实现,是 react 生态的快速建立让它正式进入了广大开发者的视角。
在正式开始前,抛出几个问题来引导思路,这些问题也会在不同的小节中,逐步解决:
- 🤔️ 怎么理解 VDom?
- 🤔️ 如何表示 VDom?
- 🤔️ 如何比较 VDom 树,并且进行高效更新?
⚠️ 整理后的代码和效果图均存放在github.com/dongyuanxin。
如何理解 VDom?
曾经,前端常做的事情就是根据数据状态的更新,来更新界面视图。大家逐渐意识到,对于复杂视图的界面,频繁地更新 DOM,会造成回流或者重绘,引发性能下降,页面卡顿。
因此,我们需要方法避免频繁地更新 DOM 树。思路也很简单,即:对比 DOM 的差距,只更新需要部分节点,而不是更新一棵树。而实现这个算法的基础,就需要遍历 DOM 树的节点,来进行比较更新。
为了处理更快,不使用 DOM 对象,而是用 JS 对象来表示,它就像是 JS 和 DOM 之间的一层缓存。
如何表示 VDom?
借助 ES6 的 class,表示 VDom 语义化更强。一个基础的 VDom 需要有标签名、标签属性以及子节点,如下所示:
class Element {constructor(tagName, props, children) {this.tagName = tagName;this.props = props;this.children = children;}}
为了更方便调用(不用每次都写new),将其封装返回实例的函数:
function el(tagName, props, children) {return new Element(tagName, props, children);}
此时,如果想表达下面的 DOM 结构:
<div class="test"><span>span1</span></div>
用 VDom 就是:
// 子节点数组的元素可以是文本,也可以是VDom实例const span = el("span", {}, ["span1"]);const div = el("div", { class: "test" }, [span]);
之后在对比和更新两棵 VDom 树的时候,会涉及到将 VDom 渲染成真正的 Dom 节点。因此,为class Element增加render方法:
class Element {constructor(tagName, props, children) {this.tagName = tagName;this.props = props;this.children = children;}render() {const dom = document.createElement(this.tagName);// 设置标签属性值Reflect.ownKeys(this.props).forEach(name =>dom.setAttribute(name, this.props[name]));// 递归更新子节点this.children.forEach(child => {const childDom =child instanceof Element? child.render(): document.createTextNode(child);dom.appendChild(childDom);});return dom;}}
如何比较 VDom 树,并且进行高效更新?
前面已经说明了 VDom 的用法与含义,多个 VDom 就会组成一棵虚拟的 DOM 树。剩下需要做的就是:根据不同的情况,来进行树上节点的增删改的操作。这个过程是分为diff和patch:
- diff:递归对比两棵 VDom 树的、对应位置的节点差异
- patch:根据不同的差异,进行节点的更新
目前有两种思路,一种是先 diff 一遍,记录所有的差异,再统一进行 patch;另外一种是 diff 的同时,进行 patch。相较而言,第二种方法少了一次递归查询,以及不需要构造过多的对象,下面采取的是第二种思路。
变量的含义
将 diff 和 patch 的过程,放入updateEl方法中,这个方法的定义如下:
/**** @param {HTMLElement} $parent* @param {Element} newNode* @param {Element} oldNode* @param {Number} index*/function updateEl($parent, newNode, oldNode, index = 0) {// ...}
所有以$开头的变量,代表着真实的 DOM。
参数index表示oldNode在$parent的所有子节点构成的数组的下标位置。
情况 1:新增节点
如果 oldNode 为 undefined,说明 newNode 是一个新增的 DOM 节点。直接将其追加到 DOM 节点中即可:
function updateEl($parent, newNode, oldNode, index = 0) {if (!oldNode) {$parent.appendChild(newNode.render());}}
情况 2:删除节点
如果 newNode 为 undefined,说明新的 VDom 树中,当前位置没有节点,因此需要将其从实际的 DOM 中删除。删除就调用$parent.removeChild(),通过index参数,可以拿到被删除元素的引用:
function updateEl($parent, newNode, oldNode, index = 0) {if (!oldNode) {$parent.appendChild(newNode.render());} else if (!newNode) {$parent.removeChild($parent.childNodes[index]);}}
情况 3:变化节点
对比 oldNode 和 newNode,有 3 种情况,均可视为改变:
- 节点类型发生变化:文本变成 vdom;vdom 变成文本
- 新旧节点都是文本,内容发生改变
- 节点的属性值发生变化
首先,借助Symbol更好地语义化声明这三种变化:
const CHANGE_TYPE_TEXT = Symbol("text");const CHANGE_TYPE_PROP = Symbol("props");const CHANGE_TYPE_REPLACE = Symbol("replace");
针对节点属性发生改变,没有现成的 api 供我们批量更新。因此封装replaceAttribute,将新 vdom 的属性直接映射到 dom 结构上:
function replaceAttribute($node, removedAttrs, newAttrs) {if (!$node) {return;}Reflect.ownKeys(removedAttrs).forEach(attr => $node.removeAttribute(attr));Reflect.ownKeys(newAttrs).forEach(attr =>$node.setAttribute(attr, newAttrs[attr]));}
编写checkChangeType函数判断变化的类型;如果没有变化,则返回空:
function checkChangeType(newNode, oldNode) {if (typeof newNode !== typeof oldNode ||newNode.tagName !== oldNode.tagName) {return CHANGE_TYPE_REPLACE;}if (typeof newNode === "string") {if (newNode !== oldNode) {return CHANGE_TYPE_TEXT;}return;}const propsChanged = Reflect.ownKeys(newNode.props).reduce((prev, name) => prev || oldNode.props[name] !== newNode.props[name],false);if (propsChanged) {return CHANGE_TYPE_PROP;}return;}
在updateEl中,根据checkChangeType返回的变化类型,做对应的处理。如果类型为空,则不进行处理。具体逻辑如下:
function updateEl($parent, newNode, oldNode, index = 0) {let changeType = null;if (!oldNode) {$parent.appendChild(newNode.render());} else if (!newNode) {$parent.removeChild($parent.childNodes[index]);} else if ((changeType = checkChangeType(newNode, oldNode))) {if (changeType === CHANGE_TYPE_TEXT) {$parent.replaceChild(document.createTextNode(newNode),$parent.childNodes[index]);} else if (changeType === CHANGE_TYPE_REPLACE) {$parent.replaceChild(newNode.render(), $parent.childNodes[index]);} else if (changeType === CHANGE_TYPE_PROP) {replaceAttribute($parent.childNodes[index], oldNode.props, newNode.props);}}}
情况 4:递归对子节点执行 Diff
如果情况 1、2、3 都没有命中,那么说明当前新旧节点自身没有变化。此时,需要遍历它们(Virtual Dom)的children数组(Dom 子节点),递归进行处理。
代码实现非常简单:
function updateEl($parent, newNode, oldNode, index = 0) {let changeType = null;if (!oldNode) {$parent.appendChild(newNode.render());} else if (!newNode) {$parent.removeChild($parent.childNodes[index]);} else if ((changeType = checkChangeType(newNode, oldNode))) {if (changeType === CHANGE_TYPE_TEXT) {$parent.replaceChild(document.createTextNode(newNode),$parent.childNodes[index]);} else if (changeType === CHANGE_TYPE_REPLACE) {$parent.replaceChild(newNode.render(), $parent.childNodes[index]);} else if (changeType === CHANGE_TYPE_PROP) {replaceAttribute($parent.childNodes[index], oldNode.props, newNode.props);}} else if (newNode.tagName) {const newLength = newNode.children.length;const oldLength = oldNode.children.length;for (let i = 0; i < newLength || i < oldLength; ++i) {updateEl($parent.childNodes[index],newNode.children[i],oldNode.children[i],i);}}}
效果观察
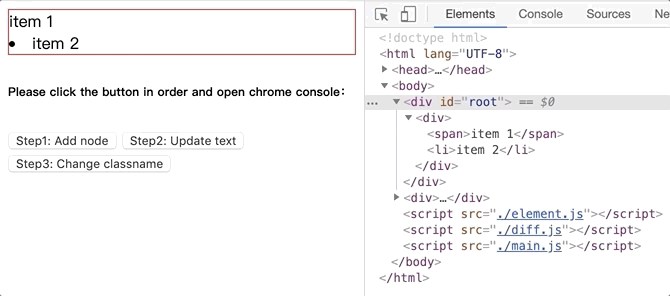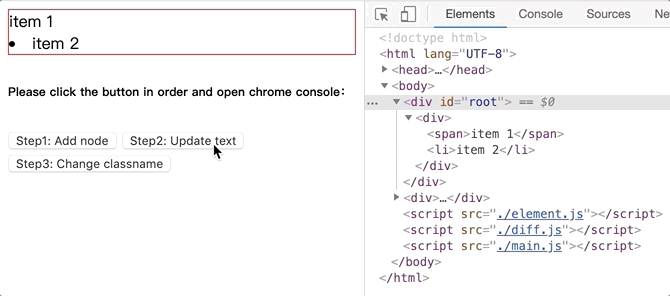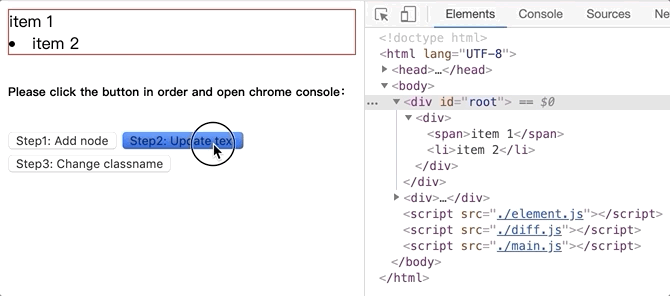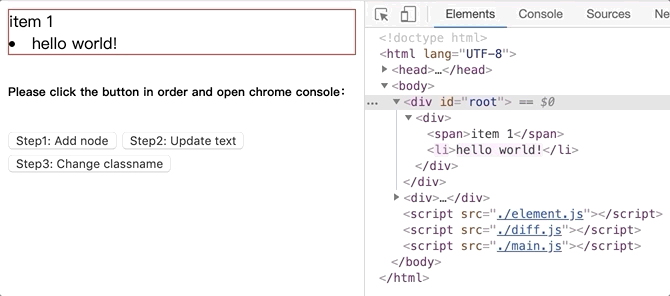
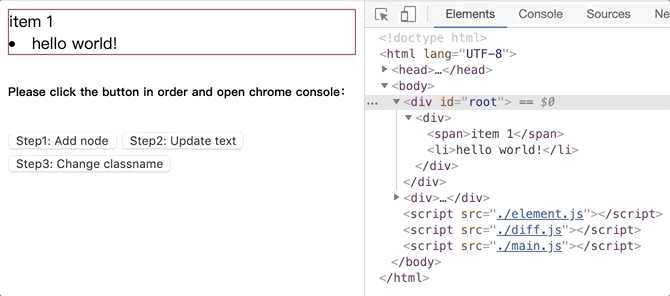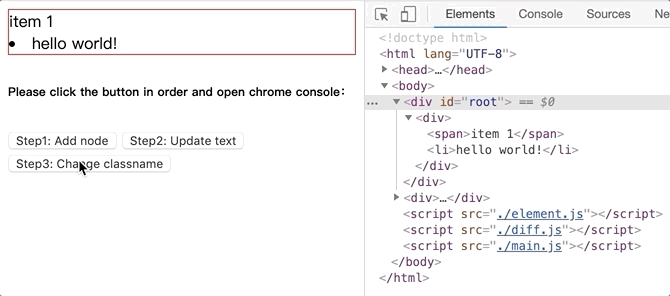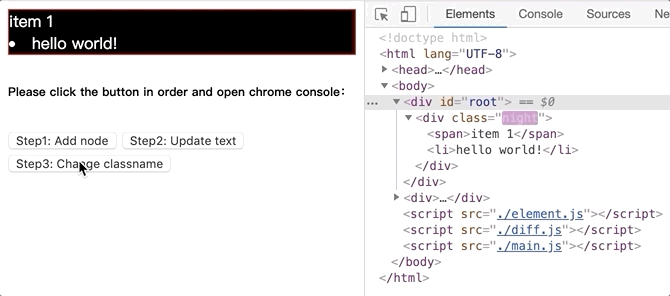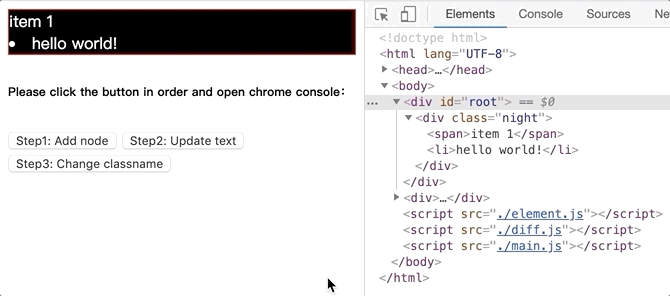
将github.com/dongyuanxin/pure-virtual-dom的代码 clone 到本地,Chrome 打开index.html。
新增 dom 节点.gif:
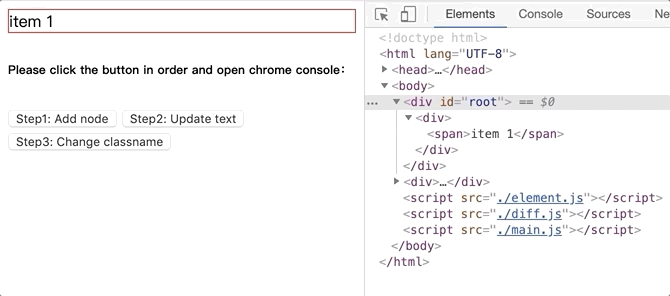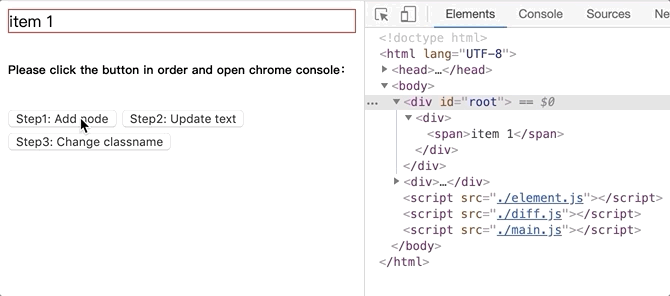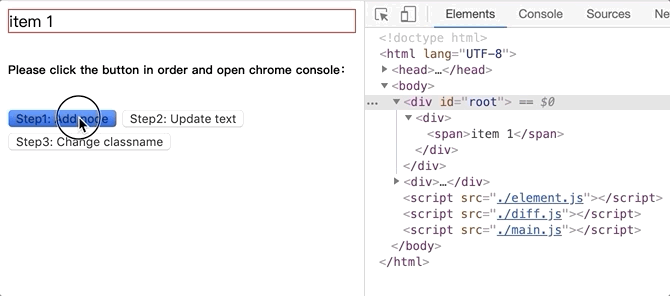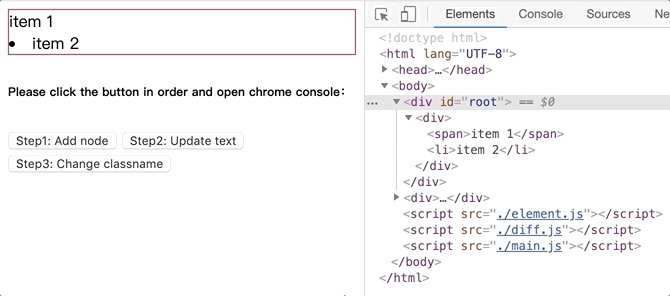
更新文本内容.gif:
更改节点属性.gif:
⚠️ 网速较慢的同学请移步 github 仓库